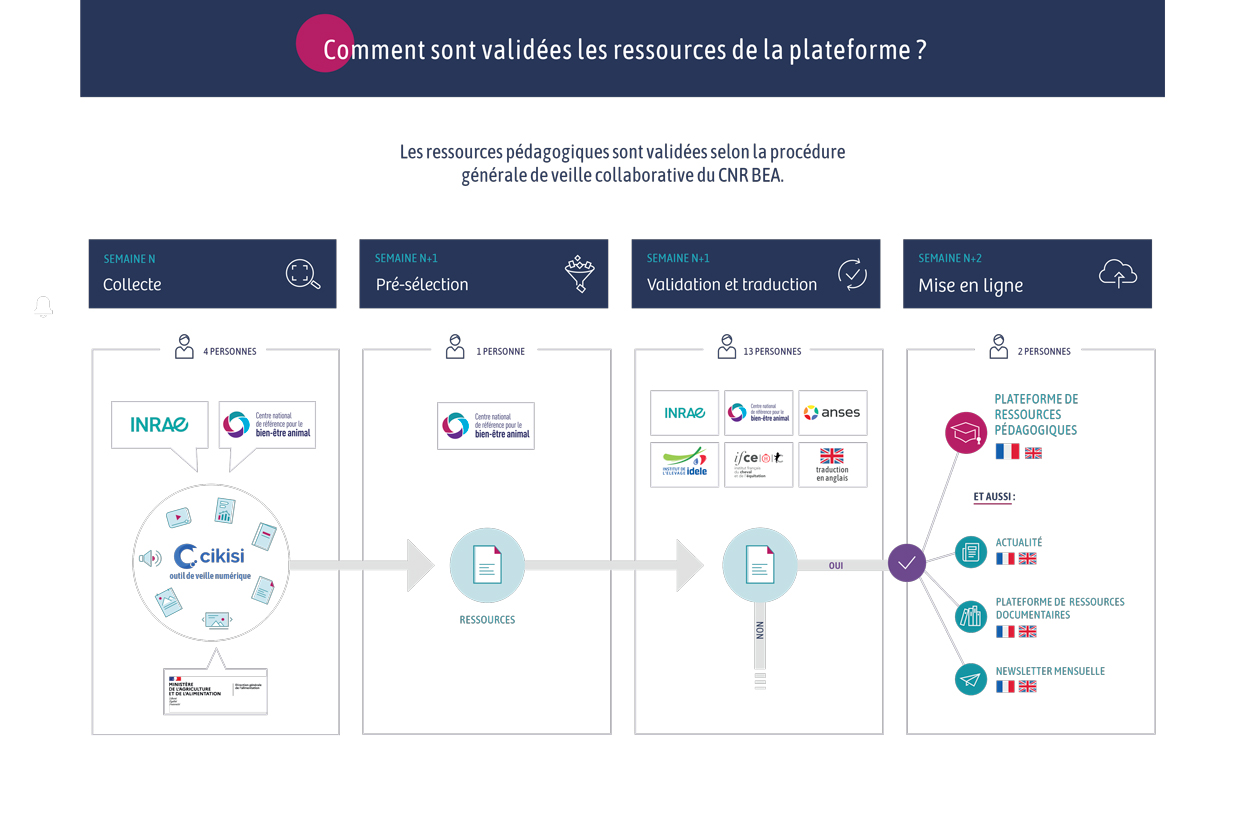
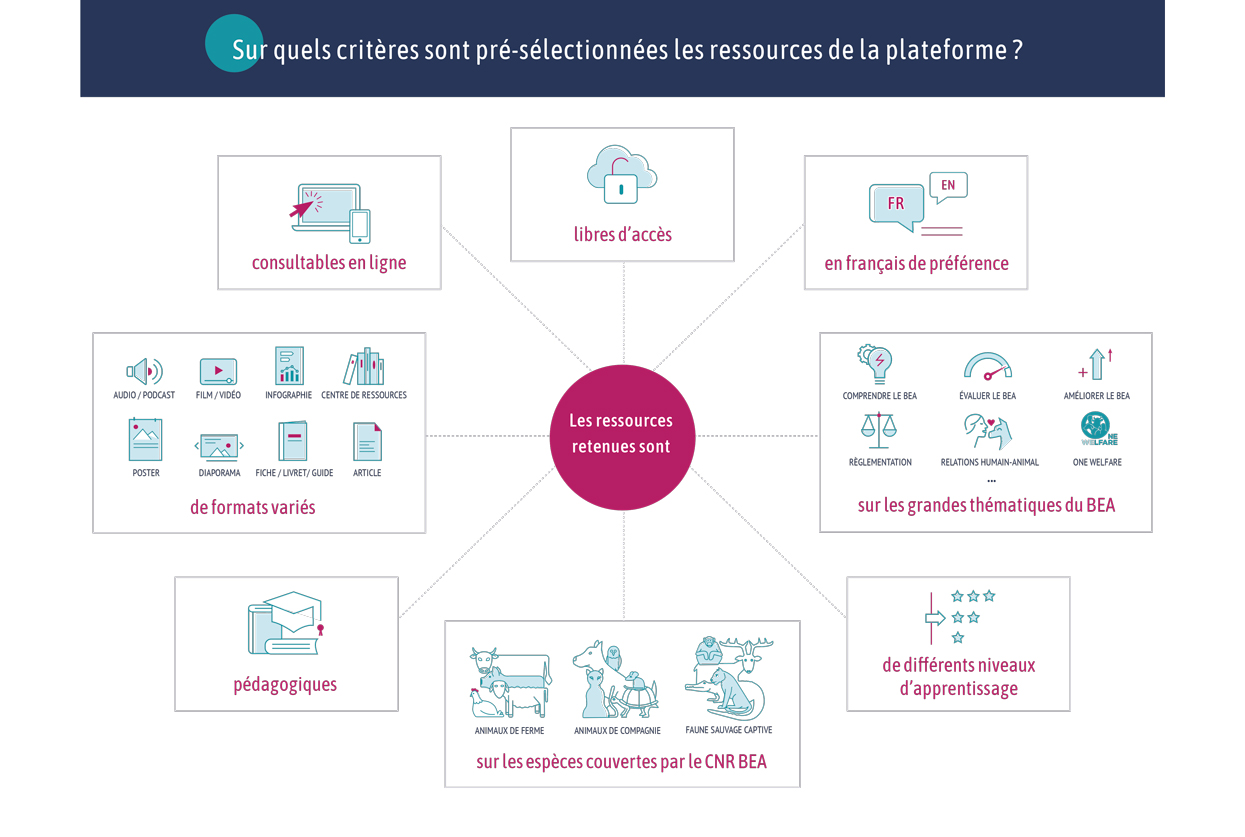
Document type : Scientific article published in the Journal of Dairy Science
Authors: Alexandra C.Green, Lena M. Lidfors, Sabrina Lomax, Livio Favaro, Cameron E.F. Clark
Preview: Mammalian vocalizations can encode contextual information in both the spectrographic components of their individual vocal units and in their temporal organization. Here we observed 23 Holstein-Friesian dairy cows immediately after birth during interactions with their calf and when their calf was separated to the other side of a fence line. We investigated whether the vocalizations emitted in these postpartum contexts would vary temporally. We also described the maternal and stress behaviors preceding and following postpartum vocal production using kinematic diagrams and characterized call sequence structure. The kinematic diagrams highlight the disruption of maternal responses caused by calf separation and show that behavioral and vocal patterns varied according to the cows' emotional states and proximity to the calf in both contexts. During calf interactions, cows mainly produced closed-mouth calls simultaneous to licking their calf, whereas an escalation of stress responses was observed during calf separation, with the cows approaching the fence line, becoming alert to the calf, and emitting more mixed and open-mouth calls. Call sequences were similarly structured across contexts, mostly containing repetitions of a single call type, with a mean interval of 0.57 s between calls and a greater cumulative vocalization duration, attributed to an increased number of vocal units per sequence. Overall, calf separation was associated with a greater proportion of calls emitted as a sequence (inverse of single isolated calls), a shorter interval between separate call sequences, and a greater number of vocal units per sequence, compared with calf interactions. These temporal vocal features varied predictably with the high stress expression from cows during calf separation and may represent temporal modulations of emotional expression. Despite the noisy farm soundscape, empirical call type and temporal vocal features were easy to measure; thus, findings could be applied to future cattle studies wishing to analyze vocalizations for on-farm welfare assessments.