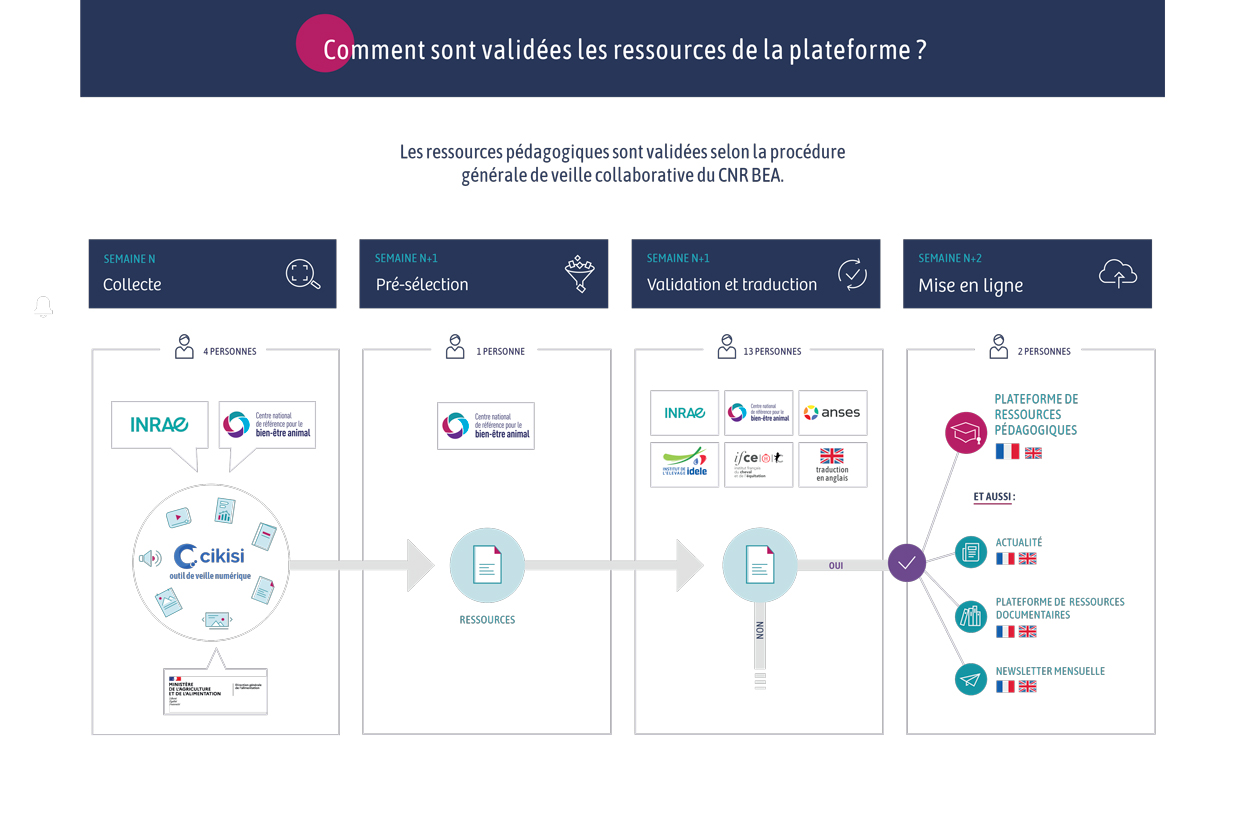
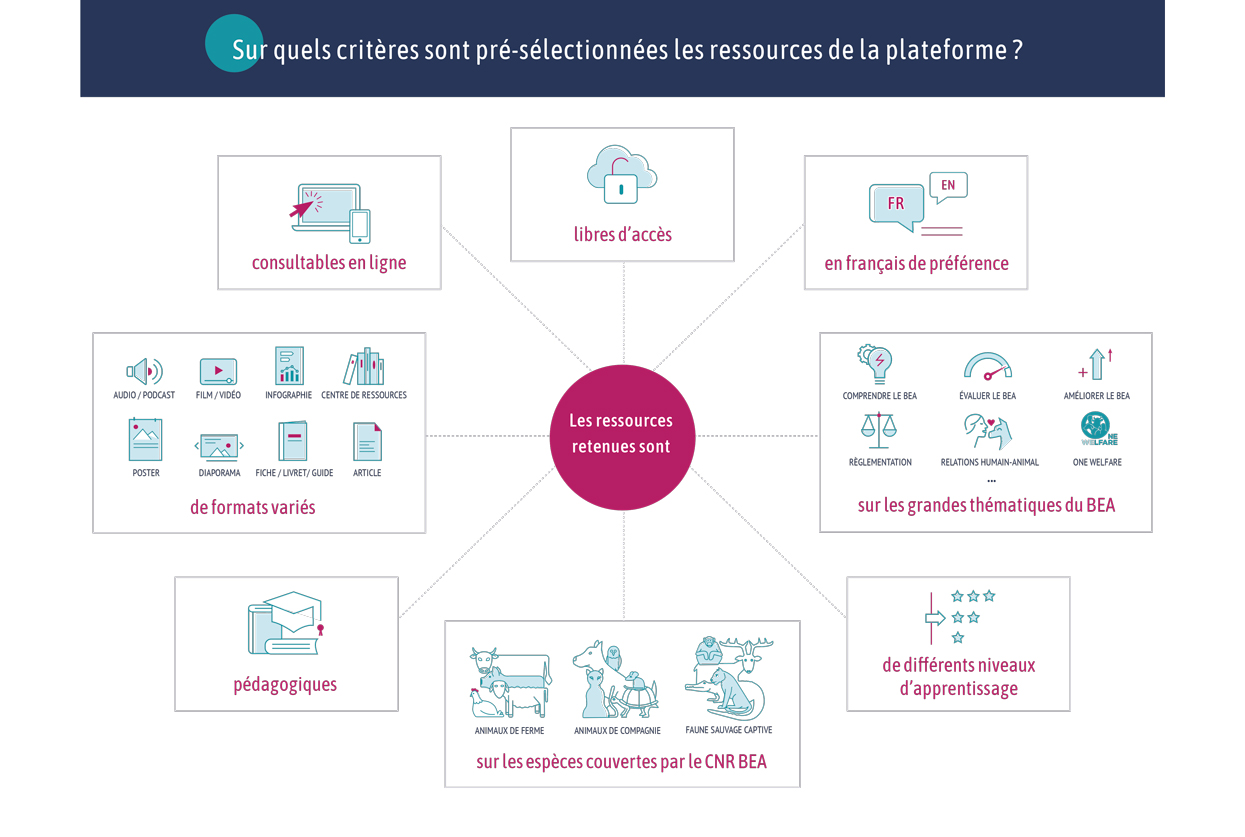
Document type: Scientific review published in Animal Production Science
Authors: Greg Underwood, Daniel Andrews, Tin Phung, Lauren E. Edwards
Preview: For modern layers to achieve optimum production performance and welfare state, the entire production process needs to be managed to achieve target bodyweight, body composition and flock uniformity. In addition to genetic improvements, flock health, environment, nutrition and on-farm husbandry practices, incubation and hatchery practices have become a focal point for producing optimum chick quality. Chick quality is a collective term involving chick size and anatomical features, physiology, robustness and liveability over the first week after placement. Chick quality is a key focus for hatcheries as this has been positively correlated with overall flock performance, especially egg production, shell quality, liveability and animal welfare. Recent advances in incubation have focussed on the benefits of all-in-all-out (single-stage) machines. Innovation in incubation systems is completely conducted today by international manufacturers, and is largely driven by the meat chicken industry. Disposal of male layer chicks has increased as a consumer welfare concern, and while investment in research and legislation changes are focussed towards providing or driving new solutions, there are currently no commercial options for industry to deal with this problem before incubation or hatch. Chick transport systems and equipment have also significantly improved in recent years, providing optimum conditions to ensure temperature uniformity and minimal moisture loss during transit before placement, thus optimising chick quality. Together, recent improvements in incubation equipment and hatchery practice can produce commercial layer chicks that are healthy, of high quality, and are then in an optimal physiological state and condition to achieve their genetic potential.